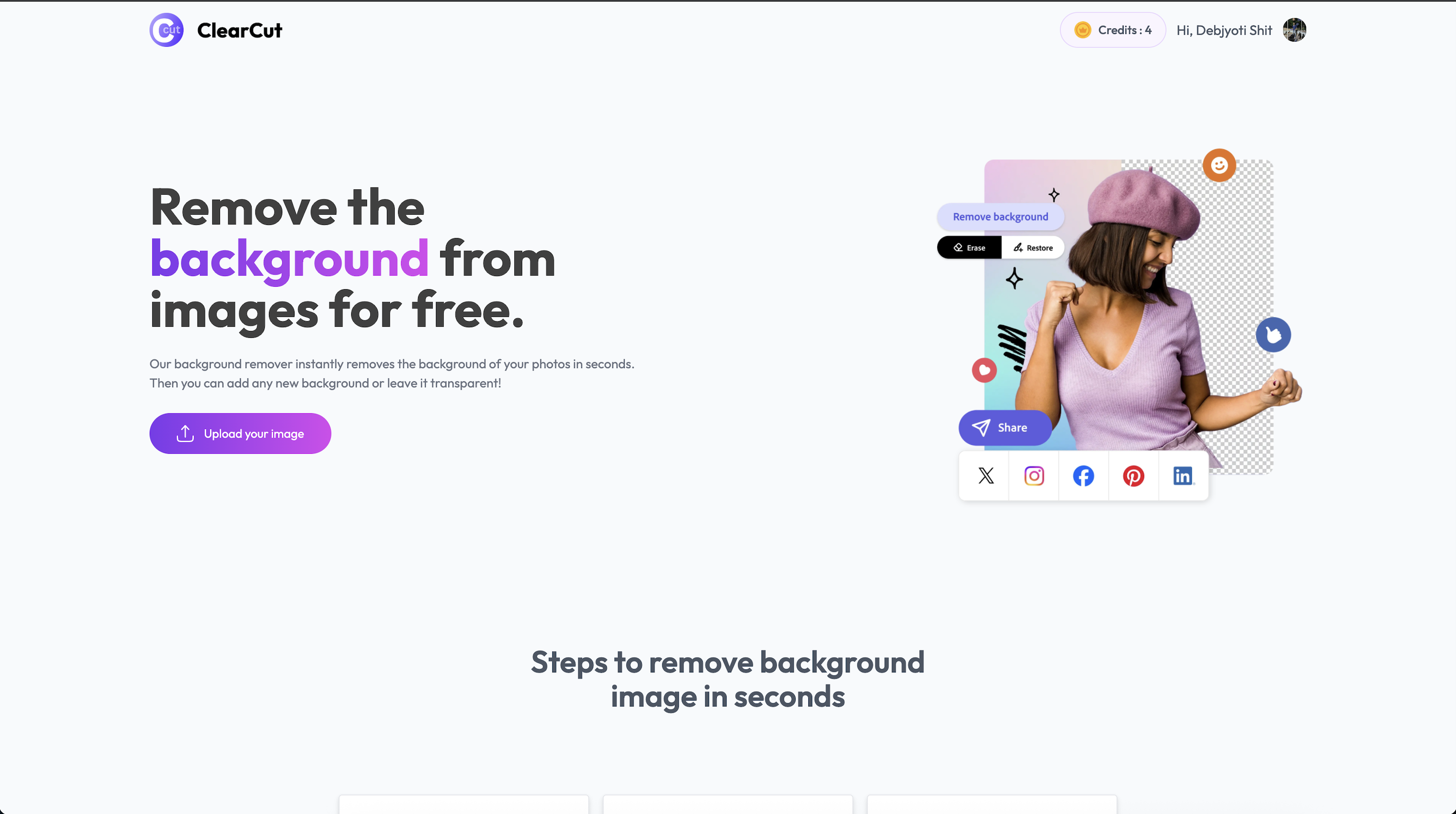
ClearCut is a full-stack AI-powered web application that removes image backgrounds and lets users download the output — all wrapped in a robust DevSecOps pipeline featuring CI/CD, security scanning, containerization, GitOps deployment, and monitoring.
Check out the live application here: clear-cut-swart.vercel.app
ClearCut is built with a DevSecOps-first mindset, ensuring secure, automated builds and deployments with visibility and control at every step.
- ✨ AI-Powered Background Removal
- 🖼️ Upload and preview images (PNG, JPG, etc.)
- ⚡ Fast and efficient processing
- 📥 One-click download of transparent images
- 🔐 Secure, automated CI/CD pipeline
- 🧪 Integrated scanning with Trivy, OWASP, and SonarQube
- 🚀 Dockerized and deployed using ArgoCD + Kubernetes
- 📊 Full observability with Grafana + Prometheus
- 📬 Gmail notifications on production deployments
- Frontend: Vite / React / JavaScript / HTML / CSS
- Backend: Node.js / Express
- Database: MongoDB
- Image Processing API: ClipDrop
- Authentication: Clerk.dev
- CI/CD: Jenkins (CI + CD Pipelines)
- Security Scans: Trivy, OWASP Dependency Check
- Code Quality: SonarQube
- Containerization: Docker
- GitOps Deployment: ArgoCD + Kubernetes (AWS EKS)
- Infrastructure as Code: Terraform, Helm
- Monitoring (Helm) & Alerts: Prometheus, Grafana, Gmail
Create the following .env files before starting the app:
MONGODB_URI = <YOUR MONGODB URI>
CLERK_WEBHOOK_SECRET = <YOUR CLERK WEBHOOK SECREL>
CLIPDROP_API = <YOUR CLIPDROP_API>VITE_CLERK_PUBLISHABLE_KEY= <YOUR CLERK PUBLISHABLE KEY>
VITE_BACKEND_URL = <YOUR BACKEND URL>git clone https://github.com/Debjyoti2004/ClearCut.git
cd ClearCutnpm installnpm run devdocker-compose -upMake sure Docker is installed and running.
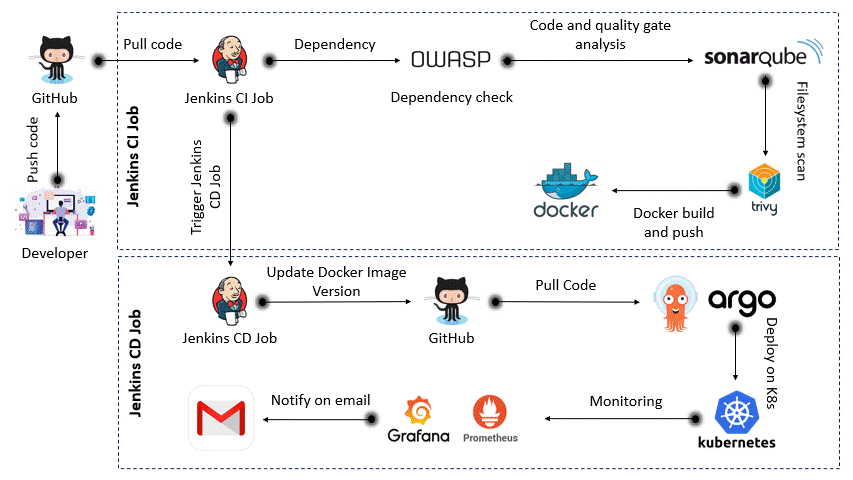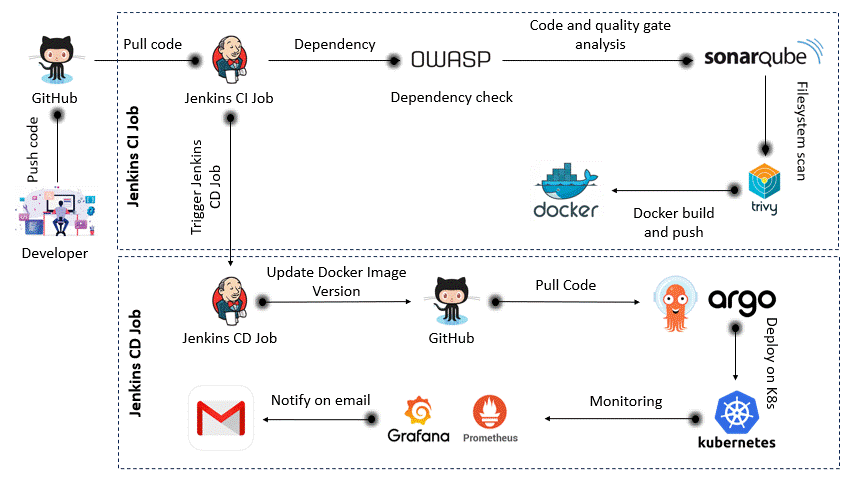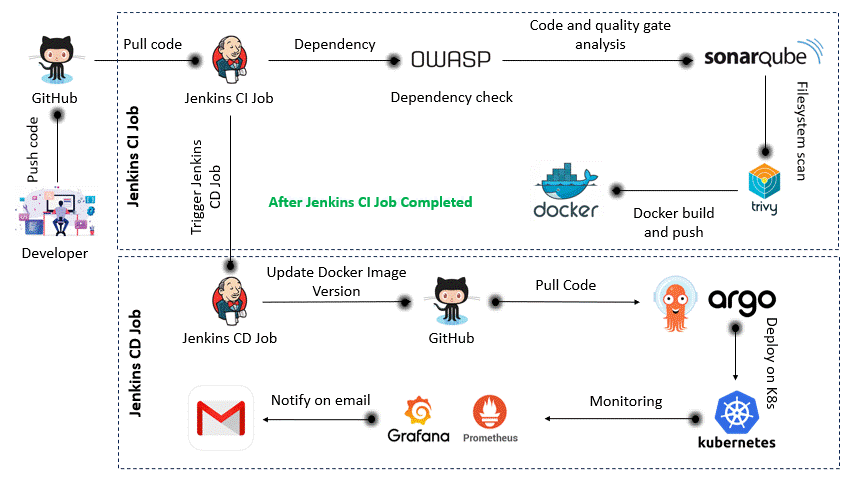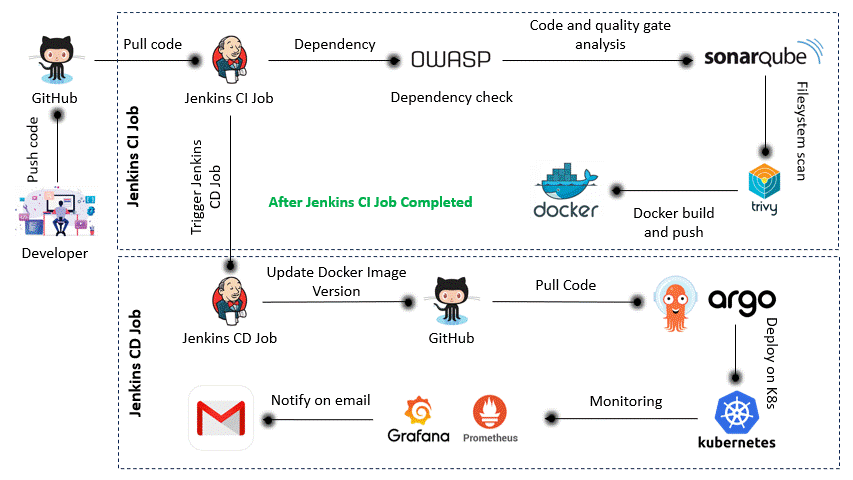
Once the app is developed and tested locally, the automated DevSecOps pipeline takes over to ensure quality, security, and smooth deployment.
- ✅ Code Commit: Developer pushes code to GitHub.
- ⚙️ Jenkins CI: Triggers automated build and testing pipeline.
- Runs dependency checks (OWASP)
- Scans vulnerabilities (Trivy)
- Code quality analysis (SonarQube)
- 🐳 Docker: Builds and pushes Docker image to registry.
- 🔁 Jenkins CD: Updates version and triggers deployment.
- 📦 ArgoCD: Pulls new version and deploys to Kubernetes.
- 🧠 Monitoring: Prometheus + Grafana monitor live performance.
- 📬 Notifications: Gmail alerts are sent post-deployment.
All steps are automated and version-controlled, ensuring production-ready, secure deployments with zero manual intervention.
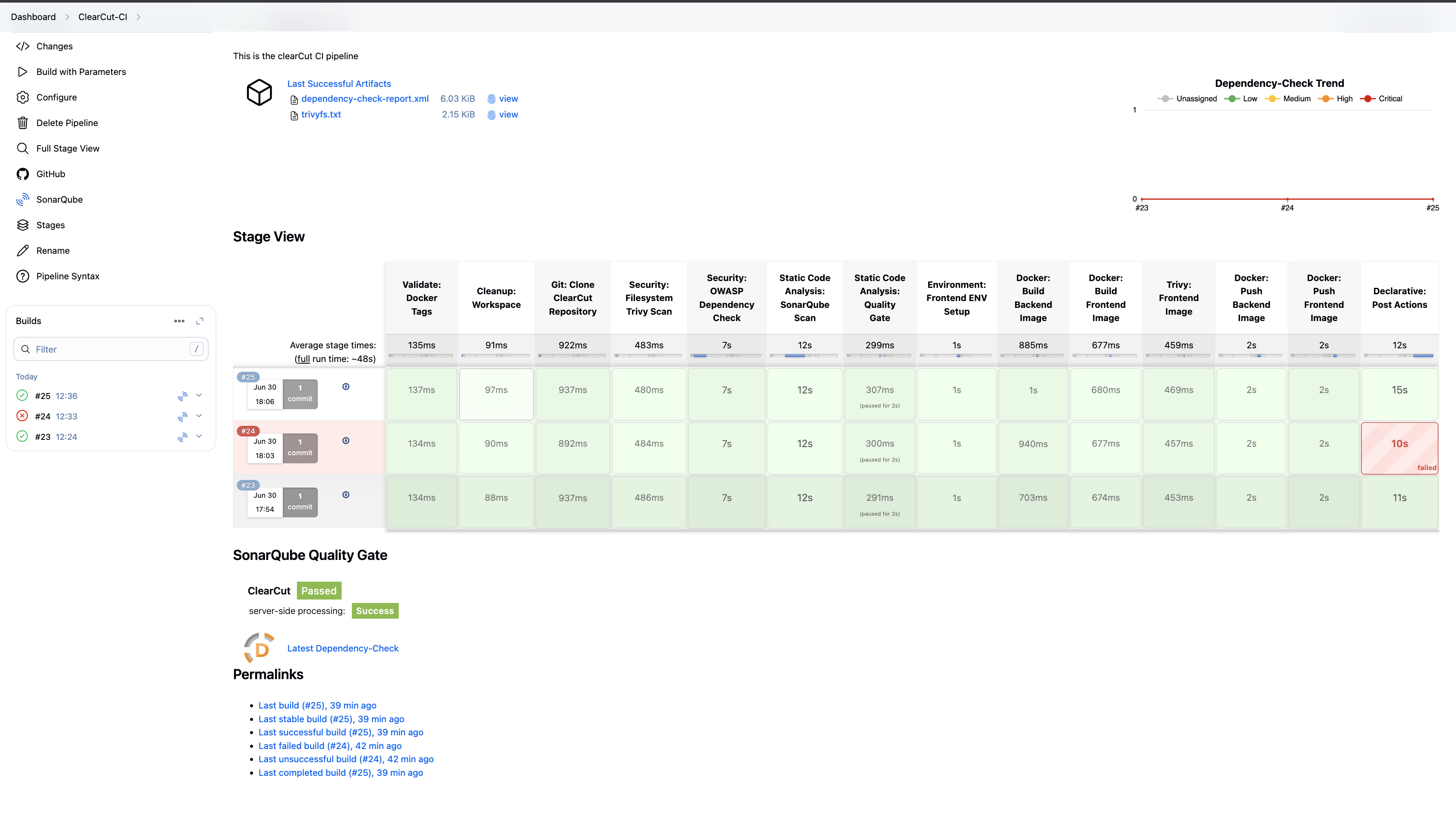
The CI pipeline is triggered when code is pushed to GitHub. It builds the project, performs security scans, and pushes the Docker image to the container registry.
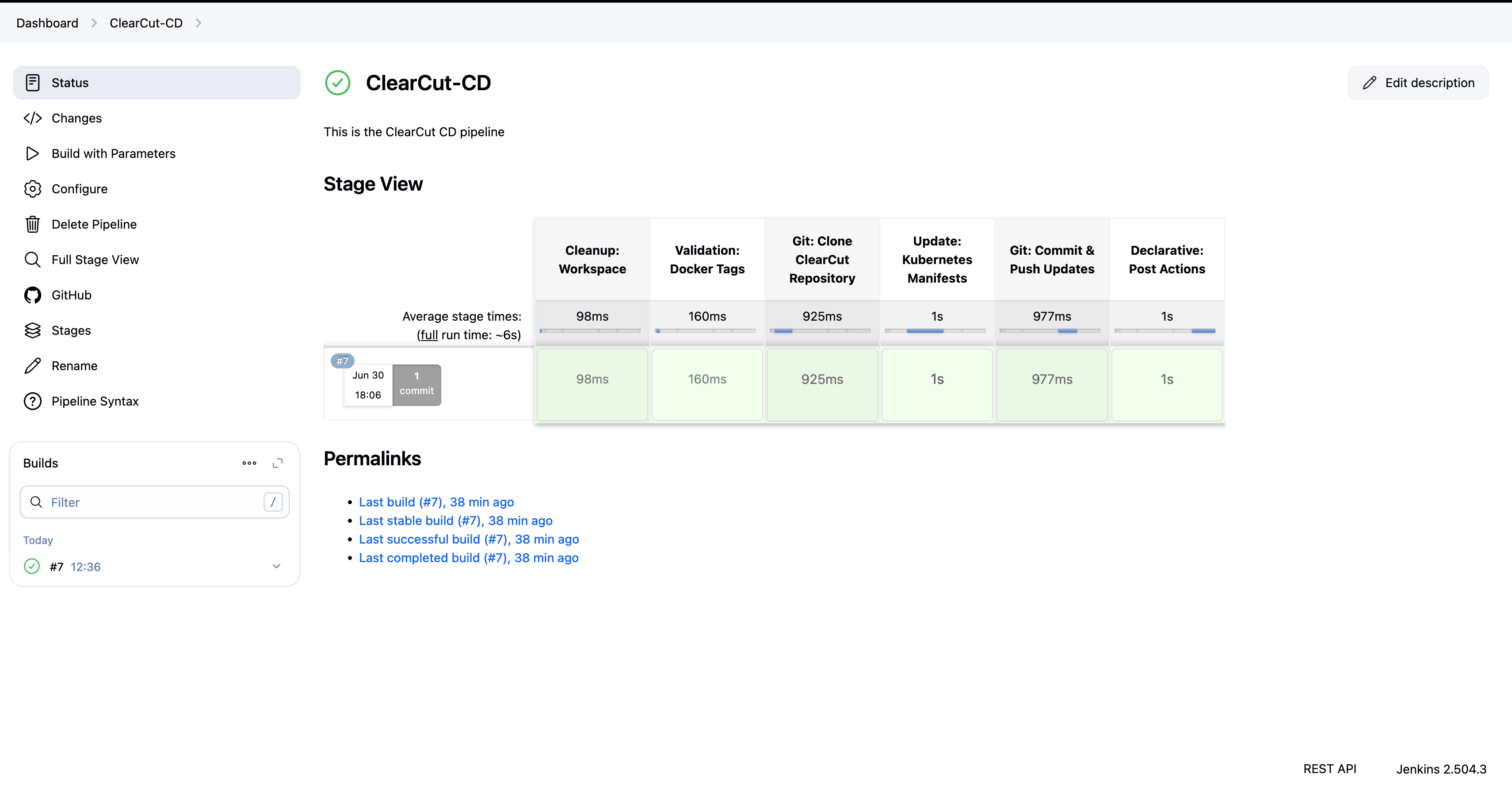
The CD pipeline pulls the latest Docker image, updates the version in GitHub, and triggers ArgoCD to deploy the application to the Kubernetes cluster.
ssh-keygen -f ClearCut-keyThis will generate ClearCut-key and ClearCut-key.pub. You'll use this to access your AWS EC2 instance.
terrafrom init
terrafrom plan
terrafrom applyAfter applying, Terraform will create:
1 EC2 instance (Ubuntu) in us-east-1 region
Instance type: t2.large (2 vCPU, 8 GB RAM)
Storage: 29 GB SSD
ssh -i ClearCut-key ubuntu@<EC2_PUBLIC_IP>sudo apt-get update -ygit clone https://github.com/Debjyoti2004/ClearCut.git
cd ClearCut/scripts
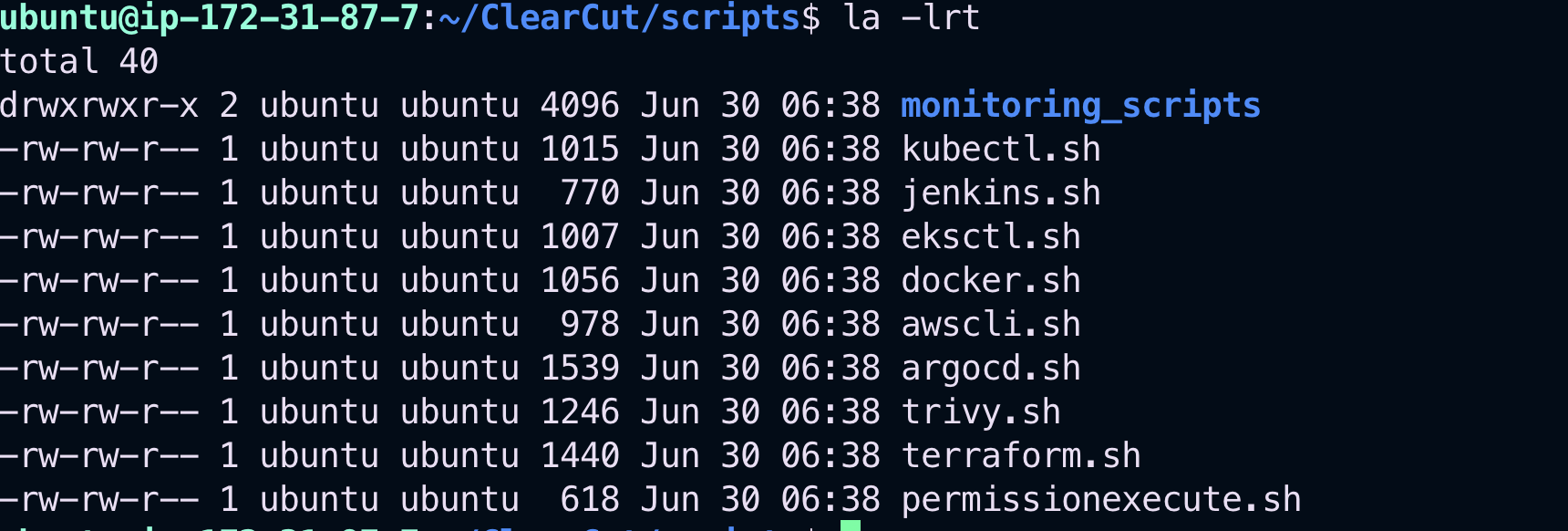
Here’s how the files look before applying execution permissions:
chmod +x permissionexecute.sh
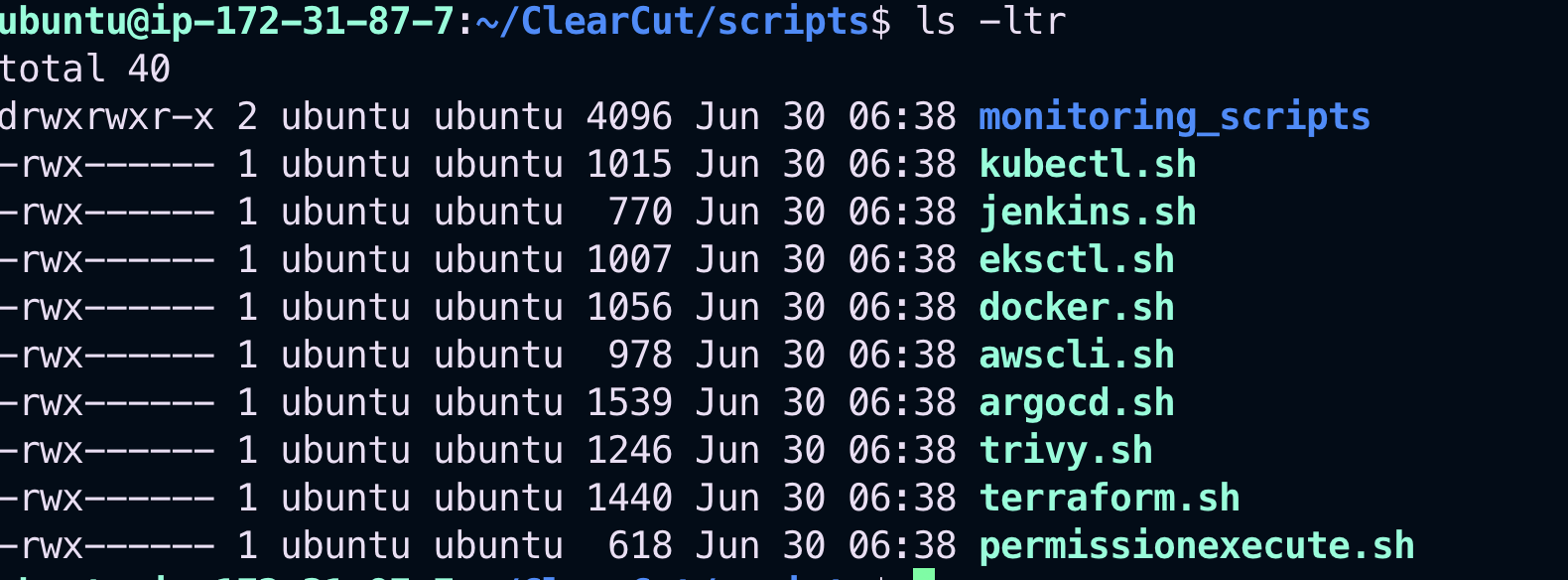
./permissionexecute.shThis script grants executable permissions to all necessary setup scripts in the folder.
You’ll see that all scripts now have executable permission:
Let's begin by installing our very first DevOps tool: Docker.
All necessary steps are scripted inside the docker.sh file — including the setup for SonarQube using Docker.
./docker.shTo run Docker without using sudo every time:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER && newgrp docker
http://<EC2_PUBLIC_IP>:9000Once Docker is up and running, install Jenkins using the provided script.
./jenkins.shhttp://<EC2_PUBLIC_IP>:8080Tip: If the page doesn't load immediately, give it a minute or two — Jenkins takes some time on the first startup.
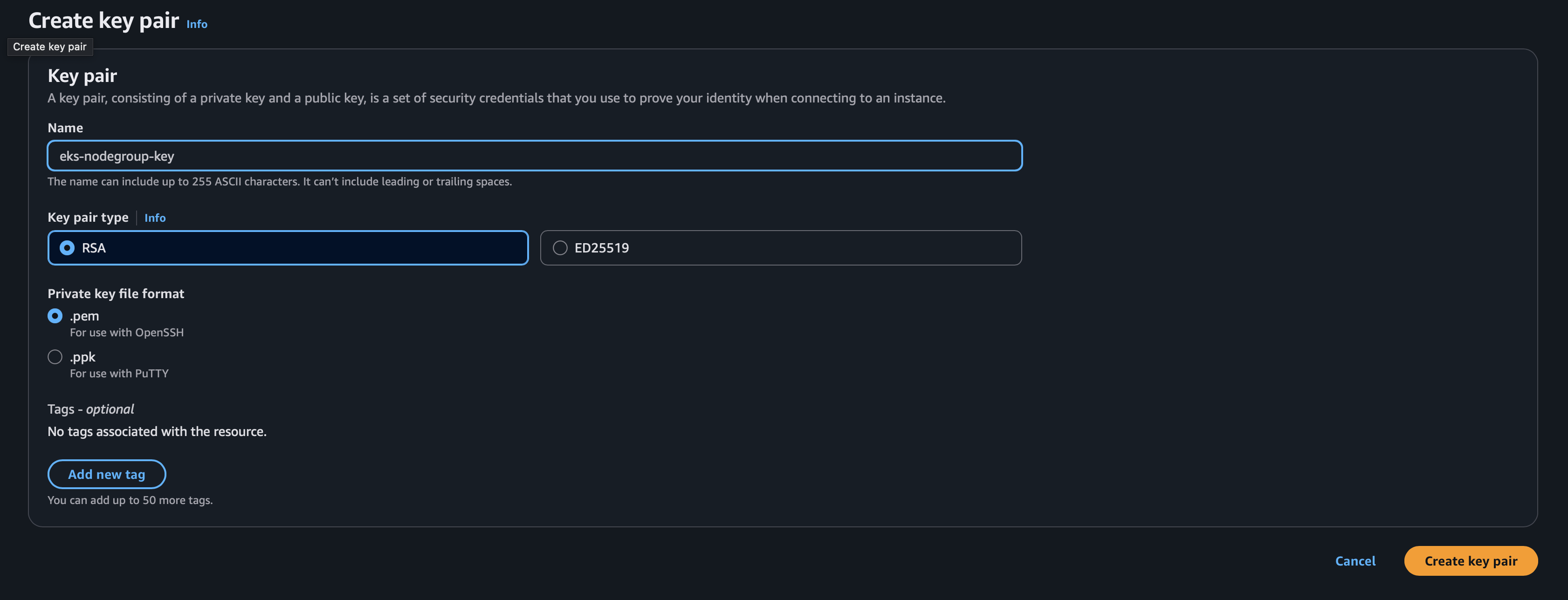
Before provisioning the EKS cluster and node groups, we need to configure some AWS tools and credentials.
This key pair will be used later to access nodes provisioned inside your EKS cluster.
- Go to the AWS Console → IAM → Create a user with programmatic access
- Attach the AdministratorAccess policy
- Download and store the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key securely
(You'll use them to configure the AWS CLI)
./awscli.shaws configureProvide the following when prompted:
AWS Access Key ID [None]: <YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID> AWS Secret Access Key [None]: <YOUR_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY> Default region name [None]: us-east-1 Default output format [None]: json
./kubectl.sh./eksctl.shOnce your AWS CLI, kubectl, and eksctl are installed and configured, you can create your EKS cluster and attach a node group.
eksctl create cluster --name=ClearCut \
--region=us-east-1 \
--version=1.30 \
--without-nodegroupThis command will create an empty EKS control plane named ClearCut in us-east-1 without any worker nodes.
OIDC is required for fine-grained IAM roles and service account integration with tools like ArgoCD, ALB Ingress Controller, etc.
eksctl utils associate-iam-oidc-provider \
--region us-east-1 \
--cluster ClearCut \
--approveThis will provision 2 EC2 instances (t2.large) and attach them to the ClearCut cluster.
eksctl create nodegroup --cluster=ClearCut \
--region=us-east-1 \
--name=ClearCut \
--node-type=t2.large \
--nodes=2 \
--nodes-min=2 \
--nodes-max=2 \
--node-volume-size=29 \
--ssh-access \
--ssh-public-key=eks-nodegroup-key kubectl get nodesTo install and run Trivy on your system, use the provided script:
./trivyThis will install Trivy and allow you to run vulnerability scans on your Docker images like so:
trivy image your-image-name./argocdThis script will:
- Install Argo CD in its own argocd namespace
- Expose the Argo CD server on a NodePort
- Install the Argo CD CLI
- Print out the exposed services and the admin password
Run this command (already included at the end of the ./argocd script):
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret \
-o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d; echo
http://<your-node-ip>:<node-port>- Username: admin
- Password: (output from above command)
Now you can log into Argo CD at:
- Now, go to User Info and update your argocd password
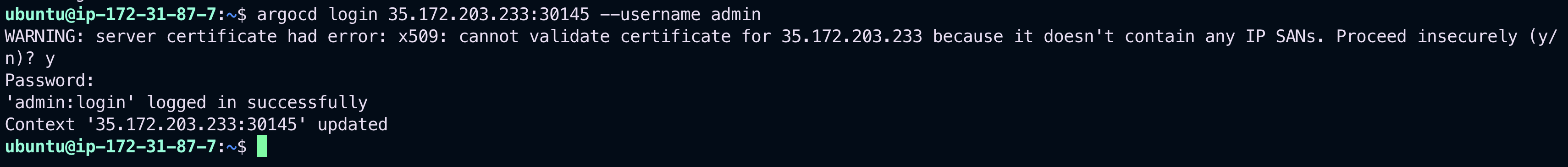
Use the following command to log in to your ArgoCD server:
argocd login <ARGOCD_SERVER> --username admin --password <PASSWORD>📷 Login Screenshot:_
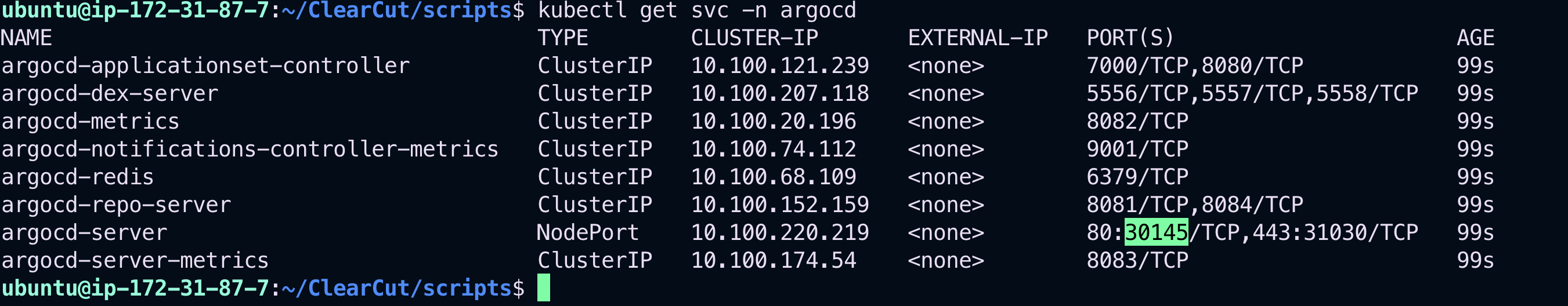
To check all the ArgoCD-related services running in your cluster:
kubectl get svc -n argocd📷 All ArgoCD Services:_
To list all registered clusters with ArgoCD:
argocd cluster list📷 ArgoCD Cluster Screenshot:_
📊 How to Monitor EKS Cluster, Kubernetes Components, and Workloads Using Prometheus & Grafana via Helm
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.shhelm repo add stable https://charts.helm.sh/stable
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo updatekubectl create namespace prometheus
kubectl get nshelm install stable prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack -n prometheusWait for a bit and check if the pods are running:
kubectl get pods -n prometheuskubectl get svc -n prometheusInitially, both services will be of type ClusterIP (not accessible externally).
By default, both services are internal. You need to expose them externally using NodePort.
Prometheus:
kubectl edit svc stable-kube-prometheus-sta-prometheus -n prometheusGrafana:
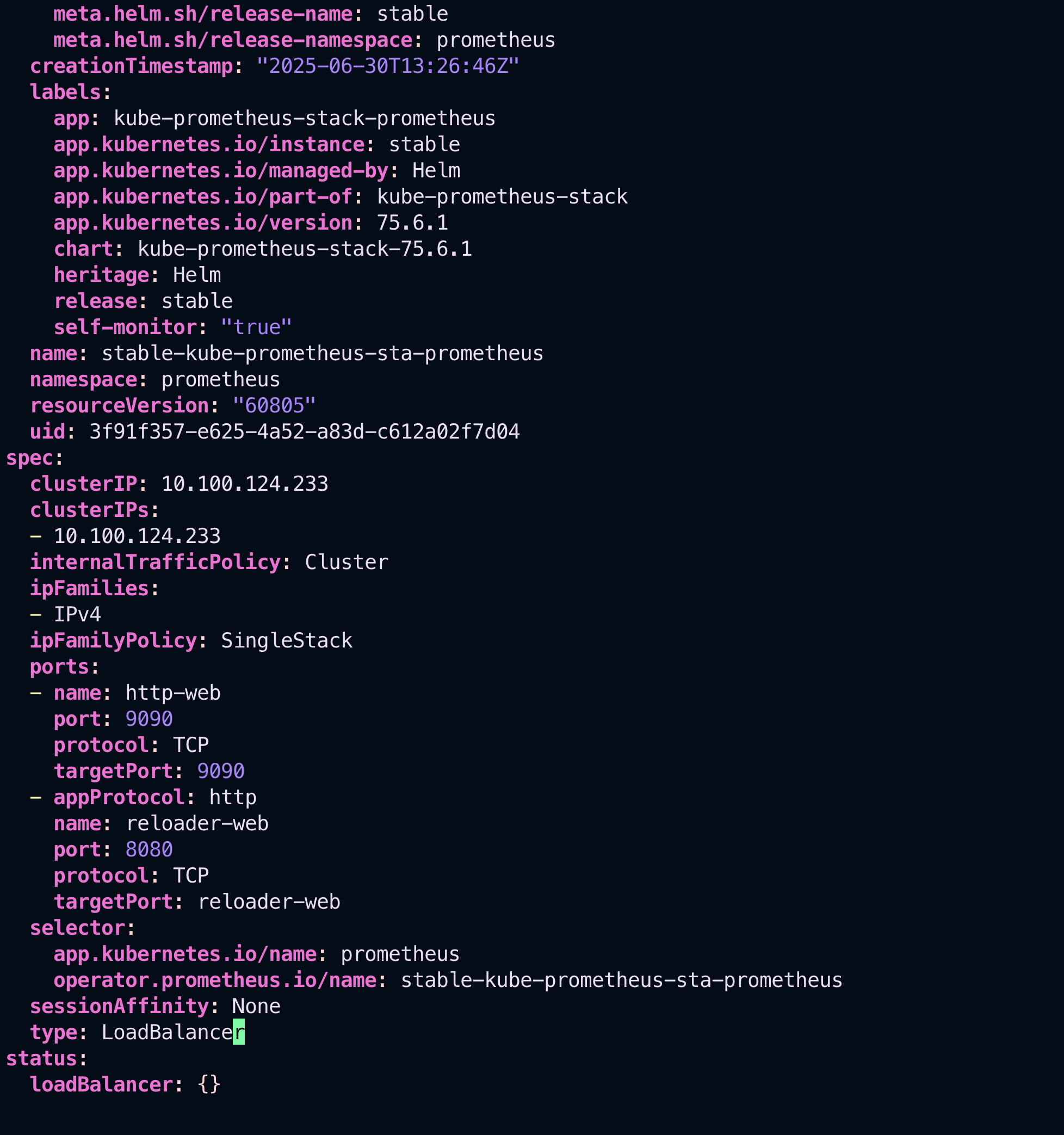
kubectl edit svc stable-grafana -n prometheusIn the YAML that opens, change:
type: ClusterIPto:
type: NodePort📷 After Changing to NodePort:
kubectl patch svc stable-kube-prometheus-sta-prometheus -n prometheus -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
kubectl patch svc stable-grafana -n prometheus -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'kubectl get svc -n prometheusLook for the NodePort value assigned to Prometheus and Grafana.
Use the EC2 public IP and NodePort to access:
- Grafana:
http://<EC2_PUBLIC_IP>:<Grafana_NodePort> - Prometheus:
http://<EC2_PUBLIC_IP>:<Prometheus_NodePort>
By default, the username is admin. You can get the password with:
kubectl get secret --namespace prometheus stable-grafana -o jsonpath="{.data.admin-password}" | base64 --decode ; echoOnce exposed, access Grafana from your browser:
To delete your cluster when done:
eksctl delete cluster --name=ClearCut --region=us-east-1Contributions, issues, and feature requests are welcome!
If you’d like to contribute to this project:
- 🍴 Fork the repository
- 🔧 Create a new branch (
git checkout -b feature/your-feature-name) - ✍️ Make your changes
- ✅ Commit your changes (
git commit -m "feat: add your feature") - 🚀 Push to your branch (
git push origin feature/your-feature-name) - 🔃 Open a Pull Request
Please make sure your code follows the project's coding style and includes relevant documentation/comments if necessary.
Thank you for helping improve this project! 💙