eFLL (Embedded Fuzzy Logic Library) is a lightweight, efficient library designed for implementing fuzzy logic systems on embedded platforms. It provides a simple yet powerful API for creating fuzzy inference systems with minimal resource overhead.
Documentation & Examples:
- Portuguese: eFLL - Uma Biblioteca Fuzzy para Arduino e Sistemas Embarcados
- English: eFLL - A Fuzzy Library for Arduino and Embedded Systems
Portable & Lightweight
- Written in C++/C using only the standard
stdlib.hlibrary - Designed for Arduino and any embedded system with C/C++ support
- No platform-specific dependencies
Flexible Architecture
- No hardcoded limits on the number of fuzzy sets, rules, inputs, or outputs
- Scalability limited only by the processing power and memory of your microcontroller
- Supports triangular, trapezoidal, and singleton membership functions
Industry-Standard Inference
- Uses MAX-MIN and Mamdani Minimum methods for inference and composition
- Implements Center of Area (COA) defuzzification in a continuous universe
- Fully tested with Google Test (GTest) framework
Step 1: Open the Arduino IDE
Step 2: Navigate to Sketch → Include Library → Manage Libraries
Step 3: Search for "eFLL" or "Fuzzy"
Step 4: Click Install
You can now include eFLL in your sketches!
Step 1: Download the library from the GitHub repository
- Click the green "Code" button and select "Download ZIP"
Step 2: Extract the ZIP file and rename the folder to "eFLL" (if needed)
Step 3: Copy the folder to your Arduino libraries directory:
- Windows:
Documents\Arduino\libraries\ - macOS:
~/Documents/Arduino/libraries/ - Linux (apt-get install):
/usr/share/arduino/libraries/ - Linux (manual install):
~/Arduino/libraries/
Step 4: Restart the Arduino IDE
Step 5: Navigate to Sketch → Include Library → eFLL
Step 1: Clone or download the repository from GitHub
git clone https://github.com/alvesoaj/eFLL.gitStep 2: Add the library files to your project
Step 3: Compile and link with your code (refer to the Makefile for examples)
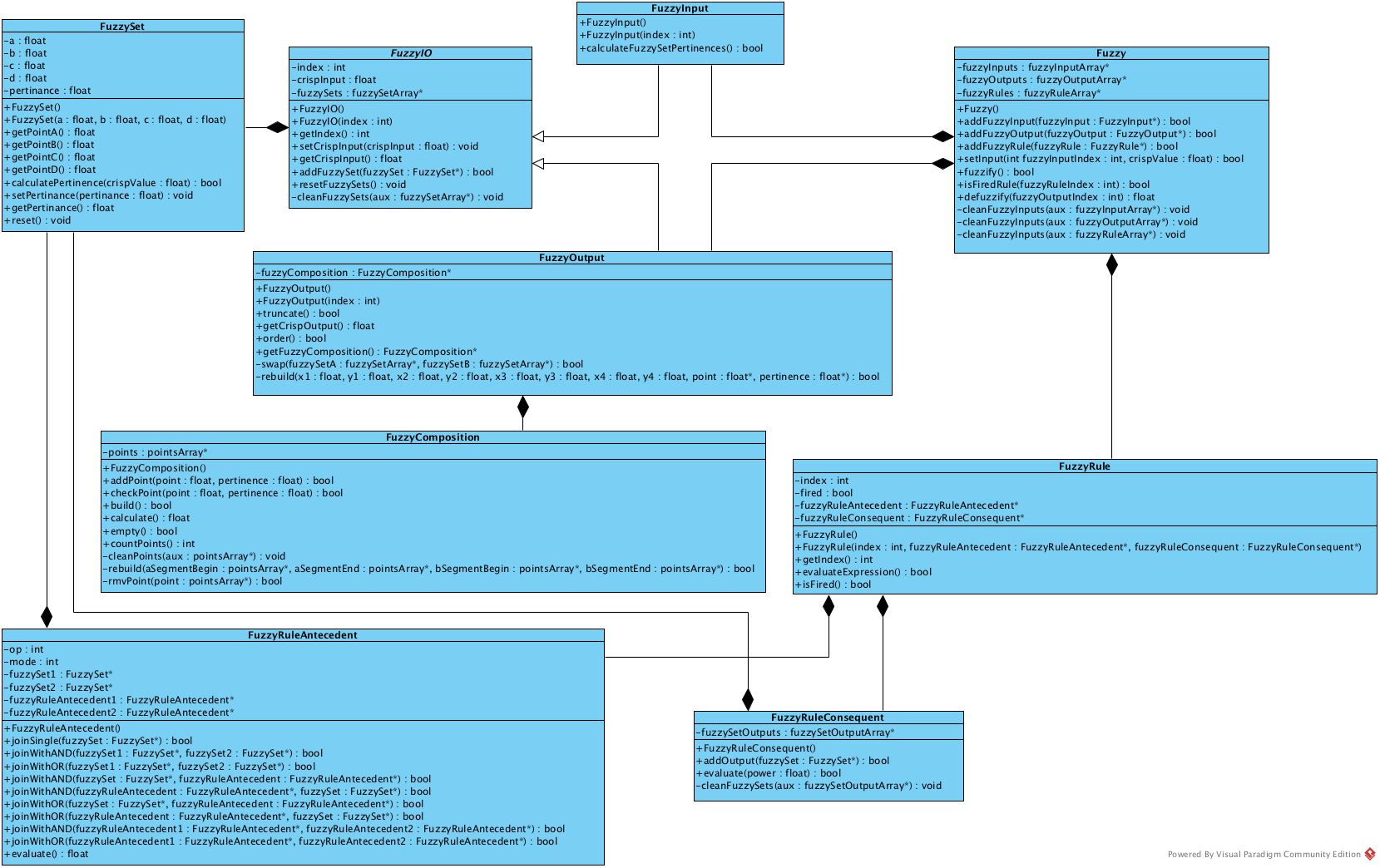
Fuzzy
- The main controller class that manages the entire fuzzy inference system
- Coordinates fuzzy sets, linguistic rules, inputs, and outputs
- Provides the primary interface for interacting with the fuzzy system
FuzzyInput
- Groups all input fuzzy sets that belong to the same input domain
- Each input variable should have its own FuzzyInput object
FuzzyOutput
- Groups all output fuzzy sets that belong to the same output domain
- Similar to FuzzyInput but used for system outputs
FuzzySet
- One of the core building blocks of the library
- Represents a membership function that models linguistic variables
- Supports three types of membership functions:
- Triangular: Three points define a triangle shape
- Trapezoidal: Four points define a trapezoid shape
- Singleton: A single point with a specific membership value
- Constructor:
FuzzySet(float a, float b, float c, float d)- Points A, B, C, D define the shape of the membership function
FuzzyRule
- Represents a single fuzzy IF-THEN rule
- Combines antecedent conditions with consequent actions
- Constructor:
FuzzyRule(int id, FuzzyRuleAntecedent* antecedent, FuzzyRuleConsequent* consequent)
FuzzyRuleAntecedent
- Defines the IF part (condition) of a fuzzy rule
- Supports AND/OR operations to combine multiple fuzzy sets
- Builds the antecedent expression for a rule
FuzzyRuleConsequent
- Defines the THEN part (action) of a fuzzy rule
- Specifies which output fuzzy sets are activated when the rule fires
- Builds the consequent expression for a rule
The fuzzy inference process involves three main steps, handled by three key methods of the Fuzzy class:
bool setInput(int id, float value);Sets a crisp input value for a specific FuzzyInput. The id parameter identifies which FuzzyInput object receives the value.
bool fuzzify();Initiates the fuzzification process, evaluates all fuzzy rules, performs composition, and prepares for defuzzification.
float defuzzify(int id);Calculates and returns the crisp output value for a specific FuzzyOutput using the Center of Area (COA) method.
// 1. Create fuzzy system
Fuzzy* fuzzy = new Fuzzy();
// 2. Define inputs and outputs
FuzzyInput* temperature = new FuzzyInput(1);
FuzzyOutput* fanSpeed = new FuzzyOutput(1);
// 3. Define membership functions
FuzzySet* cold = new FuzzySet(0, 0, 10, 20);
FuzzySet* warm = new FuzzySet(15, 25, 25, 35);
FuzzySet* hot = new FuzzySet(30, 40, 50, 50);
FuzzySet* slow = new FuzzySet(0, 0.33, 0.33, 0.5);
FuzzySet* fast = new FuzzySet(0.5, 0.66, 0.66, 1);
// 4. Add sets to inputs/outputs
temperature->addFuzzySet(cold);
temperature->addFuzzySet(warm);
temperature->addFuzzySet(hot);
fanSpeed->addFuzzySet(slow);
// 5. Create rules
FuzzyRuleAntecedent* ifCold = new FuzzyRuleAntecedent();
ifCold->joinSingle(cold);
FuzzyRuleConsequent* thenSlow = new FuzzyRuleConsequent();
thenSlow->addOutput(slow);
FuzzyRule* rule1 = new FuzzyRule(1, ifCold, thenSlow);
fuzzy->addFuzzyRule(rule1);
// 6. Run inference
fuzzy->setInput(1, 22.5); // Set temperature to 22.5°C
fuzzy->fuzzify(); // Perform fuzzification and inference
float output = fuzzy->defuzzify(1); // Get fan speedAuthor: AJ Alves alvesoaj@icloud.com
Co-authors:
- Dr. Ricardo Lira ricardor_usp@yahoo.com.br
- Msc. Marvin Lemos marvinlemos@gmail.com
- Douglas S. Kridi douglaskridi@gmail.com
- Kannya Leal kannyal@hotmail.com
Special Thanks to Contributors: @mikebutrimov, @tzikis, @na7an
MIT License