Generate programmatic tools from MCP Servers and Skills.
Agent Codemode generates programmatic tools from two sources:
- MCP Servers - Connect to any MCP server and generate typed Python bindings for its tools
- Skills - Reusable code patterns that compose multiple tools into higher-level operations
These programmatic tools can be:
- Used directly by an agent - Import generated bindings and call tools from your agent's code
- Exposed as an MCP Server - Serve the generated tools via MCP protocol for any MCP-compatible client
Traditional AI agents call tools one at a time through LLM inference. Agent Codemode enables a "Code Mode" pattern where agents write Python code that orchestrates multiple tool calls:
- More efficient: Single code generation instead of many LLM tool-call round-trips
- More reliable: Use try/except for robust error handling
- More powerful: Parallel execution with asyncio, loops, conditionals
- More composable: Save and reuse patterns as Skills
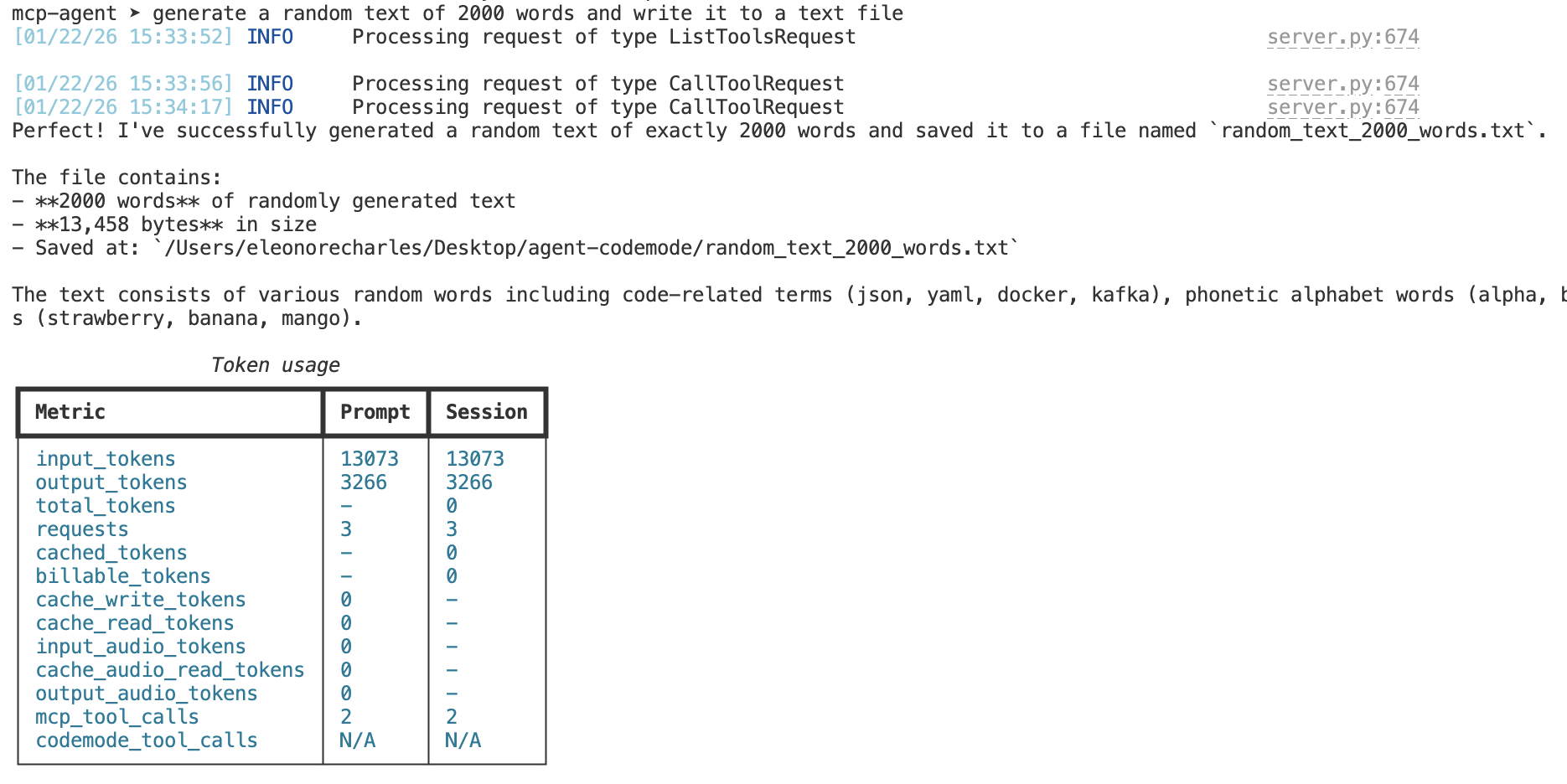
Same task, same MCP server — Code Mode uses significantly fewer tokens by composing tools in code instead of multiple LLM round-trips.
| Without Code Mode | With Code Mode |
|---|---|
 |
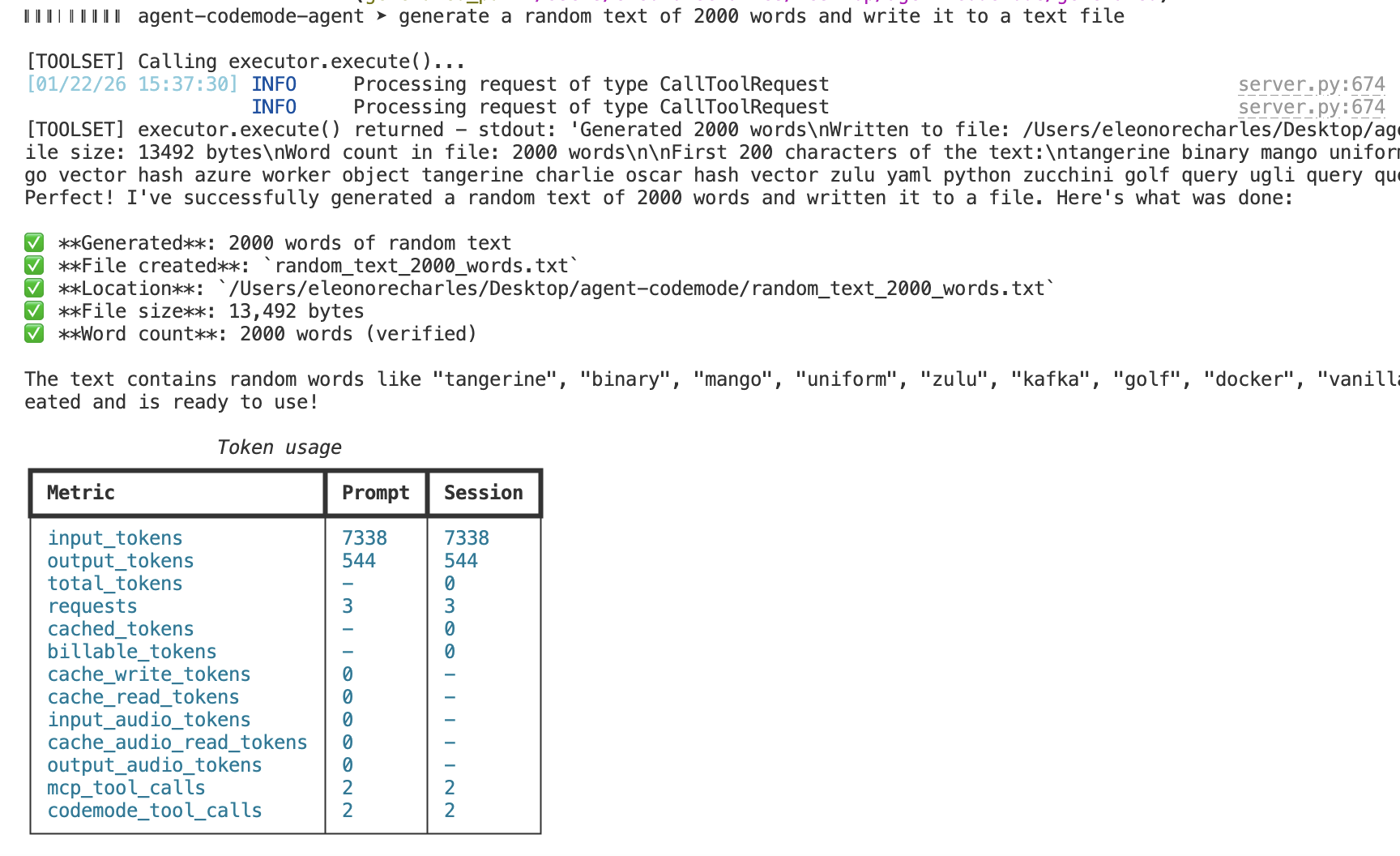 |
Prompt: "Generate 2000 words of random text and write to a file"
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
allow_direct_tool_calls |
When False (default), call_tool is hidden; all execution flows through execute_code |
max_tool_calls |
Safety cap limiting tool invocations per execute_code run |
sandbox_variant |
Sandbox type for code execution (default: "local-eval") |
workspace_path |
Working directory for sandbox execution |
generated_path |
Path where tool bindings are generated |
skills_path |
Path for saved skills |
list_tool_names: Fast listing withserver,keywords,limitfilters.include_deferred=Falseby defaultsearch_tools: Natural language search withquery,server,limit.include_deferred=Trueby defaultget_tool_details: Get full schema and documentation for a specific tool
Tools include output_schema and input_examples to improve parameter accuracy. Tools marked with defer_loading=True are excluded from default listings but included in search results.
pip install agent-codemodefrom agent_codemode import ToolRegistry, CodeModeExecutor, MCPServerConfig
# Set up registry with MCP servers
registry = ToolRegistry()
# Add an MCP server (stdio transport - uses command/args)
registry.add_server(MCPServerConfig(
name="filesystem",
command="npx",
args=["-y", "@anthropic/mcp-server-filesystem", "/tmp"]
))
# Or add an HTTP-based server
# registry.add_server(MCPServerConfig(name="web", url="http://localhost:8001"))
await registry.discover_all()
# Execute code that composes tools
async with CodeModeExecutor(registry) as executor:
result = await executor.execute("""
from generated.servers.filesystem import read_file, write_file
# Read multiple files
content1 = await read_file({"path": "/tmp/file1.txt"})
content2 = await read_file({"path": "/tmp/file2.txt"})
# Process and combine
combined = content1 + "\\n---\\n" + content2
# Write result
await write_file({"path": "/tmp/combined.txt", "content": combined})
""")Use the Tool Search Tool to discover relevant tools without loading all definitions upfront:
# Search for tools matching a description (includes deferred tools by default)
result = await registry.search_tools("file operations", limit=10)
for tool in result.tools:
print(f"{tool.name}: {tool.description}")
# Fast listing (deferred tools excluded by default)
names = registry.list_tool_names(limit=50)
# Include deferred tools explicitly
names_all = registry.list_tool_names(limit=50, include_deferred=True)Execute Python code in an isolated sandbox with auto-generated tool bindings:
async with CodeModeExecutor(registry) as executor:
execution = await executor.execute("""
import asyncio
from generated.servers.filesystem import ls, read_file
# List all files
files = await ls({"path": "/data"})
# Read all files in parallel
contents = await asyncio.gather(*[
read_file({"path": f}) for f in files
])
""", timeout=30.0)
# Outputs are available on the execution object
print(execution.stdout)
print(execution.stderr)
print(execution.text)
print(execution.success)Skills are Python files that compose tools into reusable operations. This allows agents to evolve their own toolbox by saving useful code patterns. Skills functionality is provided by the agent-skills package.
Note: Skills APIs are owned by agent-skills. Import skill utilities from agent_skills.
The primary pattern is skills as Python files in a skills/ directory:
# skills/batch_process.py
"""Process all files in a directory."""
async def batch_process(input_dir: str, output_dir: str) -> dict:
"""Process all files in a directory.
Args:
input_dir: Input directory path.
output_dir: Output directory path.
Returns:
Processing statistics.
"""
from generated.servers.filesystem import list_directory, read_file, write_file
entries = await list_directory({"path": input_dir})
processed = 0
for entry in entries.get("entries", []):
content = await read_file({"path": f"{input_dir}/{entry}"})
# Process content...
await write_file({"path": f"{output_dir}/{entry}", "content": content.upper()})
processed += 1
return {"processed": processed}Skills are imported and called like any Python module:
# In executed code
from skills.batch_process import batch_process
result = await batch_process("/data/input", "/data/output")
print(f"Processed {result['processed']} files")For programmatic skill management, use the SimpleSkillsManager:
from agent_skills import SimpleSkillsManager, SimpleSkill
# Create a skills manager
manager = SimpleSkillsManager("./skills")
# Save a skill
skill = SimpleSkill(
name="batch_process",
description="Process files in a directory",
code='''
async def batch_process(input_dir, output_dir):
entries = await list_directory({"path": input_dir})
for entry in entries.get("entries", []):
content = await read_file({"path": f"{input_dir}/{entry}"})
await write_file({"path": f"{output_dir}/{entry}", "content": content.upper()})
''',
tags=["file", "batch"],
)
manager.save_skill(skill)
# Load and use a skill
loaded = manager.load_skill("batch_process")
print(loaded.code)See the runnable examples in examples/.
python examples/simple/codemode_example.py
python examples/simple/codemode_patterns_example.pyInteractive CLI agent with Agent Codemode support:
# Standard mode
python examples/agent/agent_cli.py
# Codemode variant (code-first tool composition)
python examples/agent/agent_cli.py --codemodeUse the CodemodeToolset for direct integration with Pydantic AI agents:
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from agent_codemode import CodemodeToolset, ToolRegistry, MCPServerConfig
# Set up registry
registry = ToolRegistry()
registry.add_server(MCPServerConfig(
name="filesystem",
command="npx",
args=["-y", "@anthropic/mcp-server-filesystem", "/tmp"]
))
await registry.discover_all()
# Create toolset
toolset = CodemodeToolset(registry=registry)
# Use with Pydantic AI agent
agent = Agent(
model='anthropic:claude-sonnet-4-5',
toolsets=[toolset],
)Expose the programmatic tools as an MCP server for any MCP-compatible client:
from agent_codemode import codemode_server, configure_server
from agent_codemode import ToolRegistry, MCPServerConfig, CodeModeConfig
# Create and configure registry with MCP servers to compose
registry = ToolRegistry()
registry.add_server(MCPServerConfig(
name="filesystem",
command="npx",
args=["-y", "@anthropic/mcp-server-filesystem", "/tmp"]
))
# Configure with custom settings
config = CodeModeConfig(
workspace_path="./workspace",
skills_path="./skills",
generated_path="./generated",
)
configure_server(config=config, registry=registry)
codemode_server.run()Or start with command line:
python -m agent_codemode.server --workspace ./workspaceCreate a launcher script to configure which MCP servers to compose:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
from pathlib import Path
from agent_codemode import ToolRegistry, MCPServerConfig, CodeModeConfig
from agent_codemode.server import configure, run
# Create registry and add MCP servers to compose
registry = ToolRegistry()
registry.add_server(MCPServerConfig(
name="my_server",
command=sys.executable,
args=["/path/to/my_mcp_server.py"]
))
# Configure paths
config = CodeModeConfig(
workspace_path="./workspace",
generated_path="./generated",
skills_path="./skills",
)
configure(config=config, registry=registry)
run()Then configure your MCP client to run the launcher script.
Tools exposed by the MCP server:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
search_tools |
Progressive tool discovery |
list_servers |
List connected MCP servers |
list_tool_names |
Fast listing of tool names |
get_tool_details |
Get full tool schema |
execute_code |
Run code that composes tools |
call_tool |
Direct tool invocation |
save_skill / run_skill |
Skill management |
list_skills / delete_skill |
Skill management |
add_mcp_server |
Dynamically add servers |
When building an agent that uses Codemode, use this system prompt pattern:
You are an AI assistant with access to MCP tools via Code Mode.
## Available Meta-Tools
- **list_tool_names** - Fast listing of tool names
- **search_tools** - AI-powered tool discovery (returns full definitions)
- **get_tool_details** - Get schema for a specific tool
- **execute_code** - Execute Python code in a sandboxed environment
## Execution Model
ALL tool execution must go through execute_code. Write Python code that imports
and uses the generated tool bindings:
from generated.servers.filesystem import read_file
content = await read_file({"path": "/data/config.json"})
print(content)
- Discover tools using search_tools or list_tool_names
- Write Python code that imports tools from generated.servers.
- Execute using execute_code
See the Getting Started guide for a complete system prompt example.
Instead of loading all tool definitions upfront (which can overwhelm context), use the Tool Search Tool pattern for progressive discovery based on the task at hand.
Compose tools through code instead of reading all data into LLM context. This is faster, more reliable (no text reproduction errors), and more efficient.
Code allows models to implement complex control flow: loops, conditionals, waiting patterns, and parallel execution without burning through context with repeated tool calls.
When running in a sandbox, state can persist between execute_code calls within the same session. Variables, functions, and imported modules remain available for subsequent code executions. Skills can also be saved to disk and loaded later for reuse across sessions.
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Agent Codemode │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ ┌───────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Tool Registry │ │ Code Executor │ │ CodemodeToolset │ │
│ │ - Discovery │ │ - Sandbox │ │ (Pydantic AI) │ │
│ │ - Search │ │ - Bindings │ │ - search_tools │ │
│ │ - Cache │ │ - Execute │ │ - execute_code │ │
│ └─────────────────┘ └────────────────┘ └───────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌───────────────┴───────────────┐ │
│ │ Generated Bindings │ │
│ │ generated/servers/<name>.py │ │
│ └───────────────────────────────┘ │
├────────────────────────────────┬────────────────────────────────────┤
│ MCP Servers │ Agent Skills (agent_skills) │
│ (filesystem, bash, web, etc. │ (SimpleSkillsManager, │
│ connected via MCP protocol) │ SkillDirectory, skills/*.py) │
└────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────────────────┘
- Introducing Code Mode - Cloudflare
- Code Execution with MCP - Anthropic
- Programmatic Tool Calling - Anthropic
- Advanced Tool Use - Anthropic
- Programmatic MCP Prototype
BSD 3-Clause License