- Open the command line
- To check to see if you have git installed
git --version
- To install on a Mac, type (this will install a pared down version of XCode that includes git)
xcode-select --install
- For other operating systems, following these directions
- Go to GitHub to create an account
- Go to UO Data Science
- Add username to list on Slack to be added to the organization
- Accept email invitation
- To have a backup
- To be able to roll back to any previous version
- To work collaboratively and avoid conflicted copies
- To document your code and improve reproducibility
- To make it simple to share your code
- To avoid this:
- Snapshots = records what the files look like at a given point in time
- You decide when to take snapshots
- History of all snapshots is retained
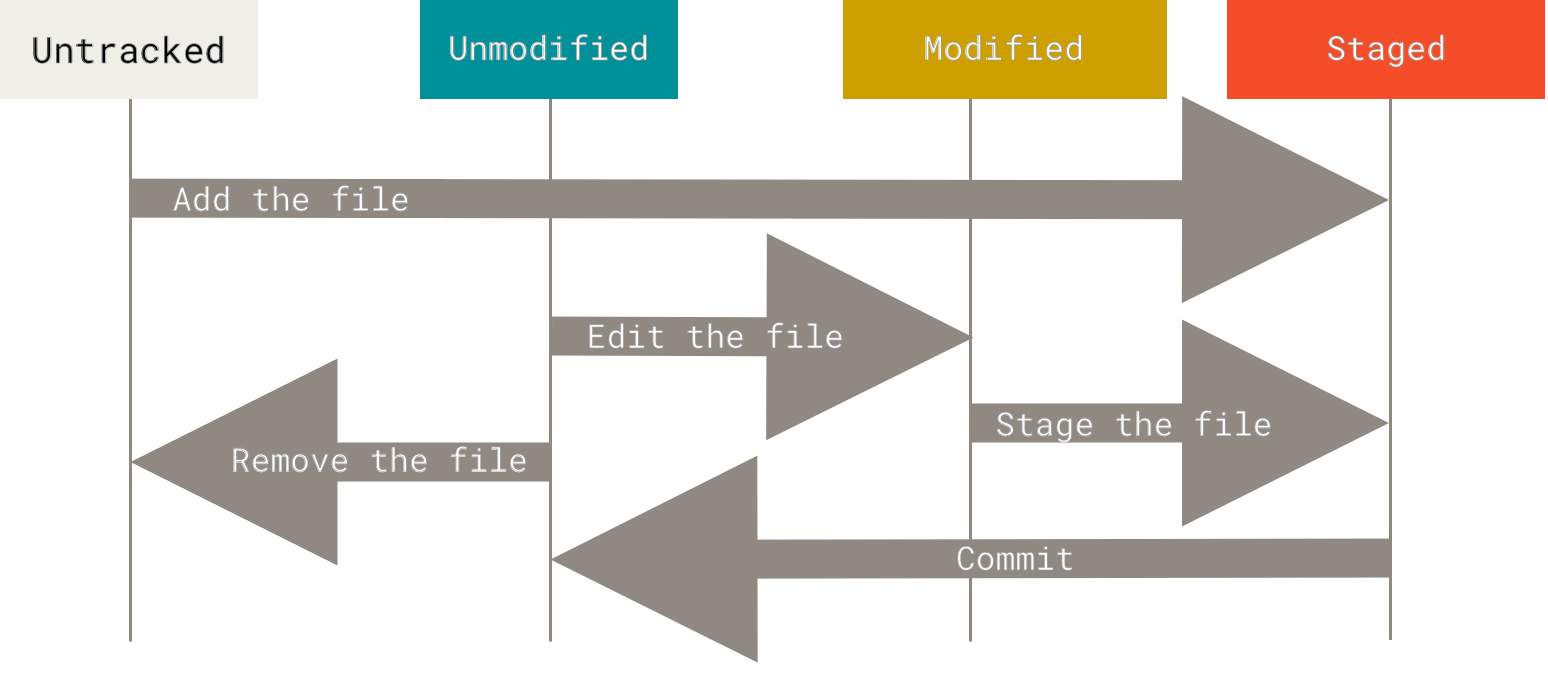
- Staging = which files to include in the snapshot
- You decide which files you want to take snapshots of
- Commit = the act of creating a snapshot
- Info that's been changed
- A reference to the commit that came brefore it (parent commit)
- Repository = collection of files and file history
- Local repository = exists only on your local machine
- Remote repository = exists on a remote website (e.g. github.com, gitlab.com, bitbucket.org)
- Cloning = copying a repository
- Pulling = grabbing changes from the original repository
- Pushing = pushing changes to the original repository
- Branches = offshoots of the master branch
- Master = typically the main branch
- Merging = combining branch with master repository
- Make changes to a file
- Stage the file
- Choose to take a snapshot of the changes
git add [file]
- Commit the changes
- Take a snapshot of the file
git commit -m "I made these changes.." [file]
- Rinse, repeat.
- Make directory on your desktop
mkdir ~/Desktop/git-test
cd ~/Desktop/git-test- Initialize the repository
git init- Check what's in the directory
ls -a- Get status
git status- Create file
printf "I <3 git" > test.txt- Check status
ls
git status- Add test.txt file to the repository
git add test.txt - Check status
git status- Save snapshot of repo by commiting changes
git commit -m "added test file"- Check version history
git log- Pull recent changes from remote repository
- Get most up to date version of the repository
git pull
- Make changes to a file
- Stage the file
- Choose to take a snapshot of the changes
git add [file]
- Commit the changes
- Take a snapshot of the file
git commit -m "I made these changes.." [file]
- Push changes to remote repository
- Apply your local changes to the repository
git push
- Rinse, repeat.
- Update global configurations
git config --global --list
git config --global user.name 'Dani Cosme'
git config --global user.email 'dani.cosme@gmail.com'
git config --global core.editor 'sublime'- Clone git-tutorial repo
cd ~/Desktop
git clone https://github.com/uodatascience/git-tutorial.git- Check status
git status- Get most up to date version of the repo
git pull- Open favs.txt file with text editor
# open in text editor app
open /Applications/TextEdit.app favs.txt
# open in terminal using vim
vim favs.txt- Add your favorite R package and save file
# add txt directly from command line
printf "\ndplyr" >> favs.txt- Add favs.txt to the staging area
git add favs.txt- Commit changes
git commit -m "added fav package"- Push changes to github repo
# single master branch
git push
# multiple branches
git push origin [branch name]- Pull newest version from the github repo
# single master branch
git pull
# multiple branches
git pull origin [branch name]# initialize repository
git init
# add file(s)
git add [file] # single file
git add . # all files
# make a snapshot of repository
git commit -m "[message text]"
# copy existing repository
git clone [repo address]
# get newest version of repository
git pull
# push changes to repository
git push
# view history
git log
# check changes that have been made to files in a repository
git diff
# create new branch
git checkout -b [name of new branch]
# switch branches
git checkout
# check configurations
git config --global --list